What Is Osteoarthritis (OA)?
About Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a type of degenerative joint disease that can cause joint stiffness, pain, loss of range of motion and even swelling in your joints. Osteoarthritis results from the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of bones being worn down over time.
In Osteoarthritis, the slippery surface of the cartilage becomes rough so that as the cartilage wears down completely, you may be left with bone rubbing on bone. You are at greater risk for developing Osteoarthritis as you grow older, but also if you smoke or are overweight.
A special type of osteoarthritis known as ‘degenerative joint disease’ often develops in relatively younger people who have experienced joint injuries from playing sports or from an accident. Even injuries that occurred many years ago and seem to have healed can increase your risk of Osteoarthritis.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis can damage almost any joint in your body. However, the disorder most commonly affects joints in your hands and fingers, knees, hips, ankles, neck, lower back and spine in general. The symptoms of Osteoarthritis often develop slowly and worsen over time and can include joint pain, tenderness, stiffness, loss of flexibility and range of motion and even a grating or “cracking” sound when you use the joint. They may be most noticeable when you first wake up in the morning or when there are changes in barometric pressure from the weather pattern.

If the type of work you do places repetitive stress on a particular joint you may be a greater risk for developing OA as well.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Osteoarthritis
Often, Osteoarthritis can initially be managed with lifestyle changes, physical and other therapies, and medications. Oral medications, topical crèmes, ointments and gels can help to reduce inflammation, pain, and stiffness and may be helpful. For some patients, steroid and other types of injections may have some value as well. Exercising, achieving a healthy weight and reducing or eliminating the activities causing repetitive stress to the joints are generally the most important ways to manage Osteoarthritis. Sometimes the joint pain, stiffness and loss of flexibility may make it difficult for you to participate in the sports or other daily activities you enjoy and may become severe enough to prevent you from being able to work. When joint pain is this severe, doctors may suggest joint replacement surgery.
To learn more and get help for Osteoarthritis please Schedule an Appointment with Regenerative Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Specialist Daniel Southern, M.D. in Danbury or Wilton in Fairfield County Connecticut by calling 203-456-5717.
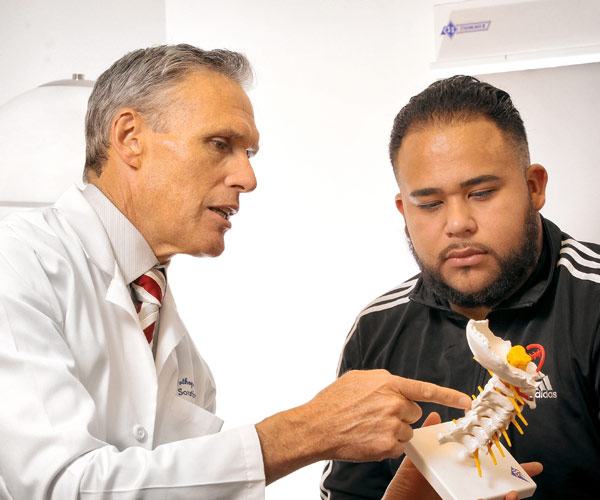

Surgical Treatment for Osteoarthritis
For those patients who are unable to achieve pain relief and improved movement in order to work and comfortably participate in the daily lifestyle activities and sports they wish to, surgery can often help by removing the most damaged tissue or re-attaching torn tendons or ligaments. In advanced cases of osteoarthritis, joint replacement can dramatically restore function.
In general, recovery time and rehabilitation from surgical treatment of arthritis can be somewhat lengthy and uncomfortable requiring careful pain management. In addition, there are some risks and possible complications of surgery including infection, excessive bleeding, blood clots, and damage to blood vessels or nerves.
To learn more and get help for Osteoarthritis please Schedule an Appointment with Regenerative Orthopedic & Sports Medicine Specialist Daniel Southern, M.D. in Danbury or Wilton in Fairfield County Connecticut by calling 203-456-5717.
Regenerative Orthopedic Medicine Treatment for Osteoarthritis
Regenerative procedures provide non-surgical treatment options for those suffering from pain related to osteoarthritis, joint injuries, spine pain, overuse conditions, and common sports injuries. These medical procedures are performed by highly-skilled doctors and are used to help reduce pain and improve function. They may help improve your quality of life, return to the activities you enjoy, and avoid the need for surgery or joint replacement*.
*DISCLAIMER: Like all medical procedures, regenerative procedures have a success and failure rate. Patient reviews and testimonials on this site should not be interpreted as a statement on the effectiveness of our treatments for anyone else.

